Types of fat present in apple and caramel – Embark on a culinary journey as we delve into the types of fat present in apples and caramel, exploring their nutritional value, health implications, and impact on these delectable treats. From the crisp bite of an apple to the velvety smoothness of caramel, discover the fascinating world of fats that enhance both flavor and well-being.
*
Types of Fat Present in Apple
Apples contain various types of fat, including saturated fat, monounsaturated fat, and polyunsaturated fat. Each type of fat has a unique nutritional value and health impact.
Saturated Fat
Saturated fat is found in small amounts in apples. It is a type of fat that is solid at room temperature and is primarily derived from animal products. Apples contain only trace amounts of saturated fat, which is generally considered unhealthy in large quantities.
Monounsaturated Fat
Monounsaturated fat is the most abundant type of fat in apples. It is a type of fat that is liquid at room temperature and is found in plant-based foods such as olive oil, avocados, and nuts. Monounsaturated fat is considered beneficial for heart health as it helps to lower LDL (bad) cholesterol and raise HDL (good) cholesterol.
Polyunsaturated Fat
Polyunsaturated fat is also found in apples, but in smaller amounts than monounsaturated fat. It is a type of fat that is liquid at room temperature and is primarily found in plant-based foods such as vegetable oils, seeds, and nuts.
Polyunsaturated fat is considered essential for human health as it cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained from food sources.| Type of Fat | Nutritional Value | Health Benefits | Potential Risks ||—|—|—|—|| Saturated Fat | High in calories and cholesterol | None | Increased risk of heart disease and stroke || Monounsaturated Fat | High in calories, but low in cholesterol | Lowers LDL cholesterol and raises HDL cholesterol | May increase the risk of weight gain || Polyunsaturated Fat | High in calories and essential fatty acids | Lowers LDL cholesterol and raises HDL cholesterol | May increase the risk of bleeding |
Types of Fat Present in Caramel
Caramel is a confectionery product that is made by heating sugar until it melts and turns brown. The type of fat used in the production of caramel can have a significant impact on the texture, flavor, and shelf life of the final product.
Saturated Fats
Saturated fats are the most commonly used type of fat in the production of caramel. They are solid at room temperature and have a high melting point. This gives caramel made with saturated fats a firm texture and a long shelf life.
Apples and caramel both contain healthy fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. These fats can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. If you’re looking for a delicious and healthy way to enjoy these fats, try making your own Greek yogurt.
Click here for a simple recipe. Greek yogurt is a great source of protein and calcium, and it can be used in a variety of recipes. It’s also a good way to get your daily dose of healthy fats.
| Type of Fat | Characteristics | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Butter | High in saturated fat, solid at room temperature | Firm texture, rich flavor, short shelf life |
| Lard | High in saturated fat, solid at room temperature | Firm texture, neutral flavor, long shelf life |
| Coconut oil | High in saturated fat, solid at room temperature | Firm texture, tropical flavor, long shelf life |
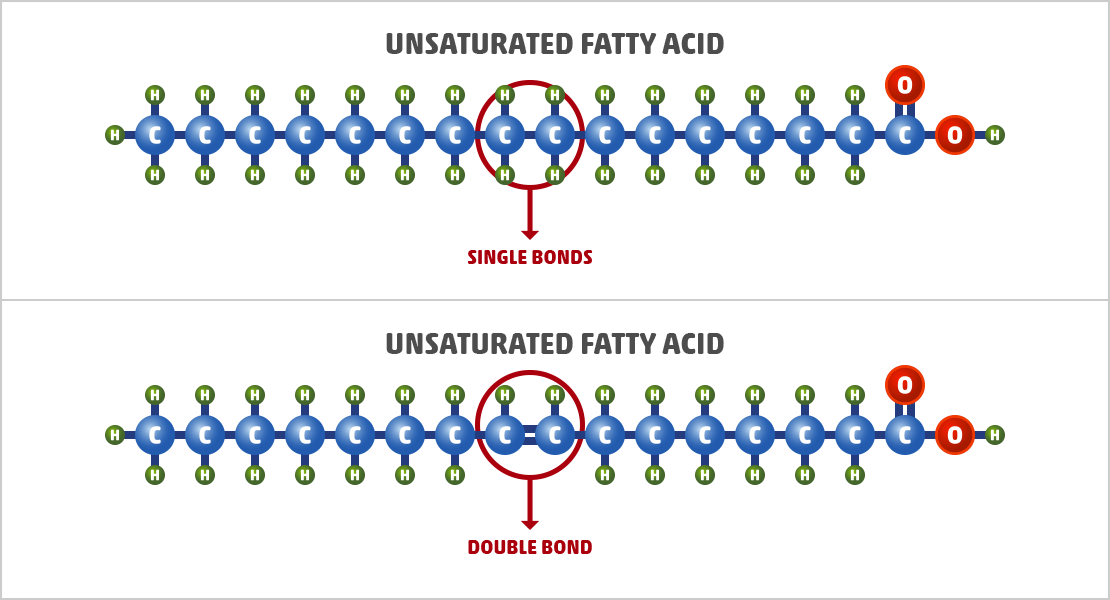
Unsaturated Fats
Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature and have a lower melting point than saturated fats. This gives caramel made with unsaturated fats a softer texture and a shorter shelf life.
| Type of Fat | Characteristics | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Vegetable oil | High in unsaturated fat, liquid at room temperature | Soft texture, neutral flavor, short shelf life |
| Olive oil | High in unsaturated fat, liquid at room temperature | Soft texture, fruity flavor, short shelf life |
| Canola oil | High in unsaturated fat, liquid at room temperature | Soft texture, neutral flavor, short shelf life |
The Impact of Fat on Caramel, Types of fat present in apple and caramel
The type of fat used in the production of caramel can have a significant impact on the texture, flavor, and shelf life of the final product. Saturated fats give caramel a firm texture and a long shelf life, while unsaturated fats give caramel a softer texture and a shorter shelf life.
The flavor of caramel can also be affected by the type of fat used, with butter and olive oil imparting a more pronounced flavor than vegetable oil or canola oil.
Comparison of Fat Content in Apple and Caramel: Types Of Fat Present In Apple And Caramel
Apples and caramel are two popular foods that are often enjoyed together. However, there is a significant difference in the fat content of these two foods.
Apples are a low-fat fruit. A medium apple contains only about 0.5 grams of fat. Caramel, on the other hand, is a high-fat food. A tablespoon of caramel contains about 2 grams of fat.
Factors Influencing Fat Content
The fat content in apples and caramel can be influenced by several factors, including:
- Variety of apple:Some varieties of apples, such as Granny Smith apples, have a higher fat content than others, such as Red Delicious apples.
- Ripeness of the apple:Riper apples have a higher fat content than unripe apples.
- Type of caramel:There are different types of caramel, such as hard caramel and soft caramel. Hard caramel has a higher fat content than soft caramel.
- Ingredients used:The ingredients used to make caramel can also affect its fat content. For example, caramel made with butter will have a higher fat content than caramel made with sugar.
Implications for Nutritional Value and Consumption
The fat content of apples and caramel has implications for their nutritional value and consumption. Apples are a healthy food that is low in fat and calories. They are a good source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Caramel, on the other hand, is a high-fat food that is high in calories.
It is not a good source of nutrients.It is important to be aware of the fat content of the foods you eat. If you are trying to lose weight or maintain a healthy weight, you should limit your intake of high-fat foods like caramel.
Health Implications of Fat Consumption from Apple and Caramel
Consuming fats from both apples and caramel has potential health implications. Understanding these implications is crucial for making informed dietary choices.
Fats play a significant role in nutrient absorption and energy production. They aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) and provide a concentrated source of energy, yielding 9 calories per gram.
Potential Health Benefits of Fat Consumption from Apples
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases:The fiber and antioxidants present in apples may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer.
- Improved digestion:The fiber in apples promotes regularity and supports a healthy digestive system.
- Weight management:Apples are a low-calorie, high-fiber fruit that can help promote satiety and support weight management efforts.
Potential Health Risks of Fat Consumption from Caramel
- Increased risk of weight gain:Caramel is a high-calorie food that can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess.
- Increased risk of dental caries:Caramel’s high sugar content can increase the risk of tooth decay.
- Allergic reactions:Some individuals may be allergic to dairy products or other ingredients used in caramel.
Importance of Moderation and Balanced Consumption
Moderation is key when consuming fats from both apples and caramel. While apples offer numerous health benefits, excessive consumption of caramel can lead to adverse effects. It is important to incorporate a variety of healthy fats into your diet, including those from fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, to ensure a balanced intake and optimal health outcomes.
Last Word
Our exploration of fat in apples and caramel concludes with a deeper understanding of the diverse roles these fats play. Whether you’re seeking nutritional insights or culinary inspiration, this guide provides a comprehensive foundation for navigating the complexities of fat in these beloved foods.
Remember, moderation and balance are key to unlocking the full potential of these culinary delights.-*

