260 celsius to fahrenheit – Embark on a journey of temperature conversion as we delve into the intricacies of converting 260 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit. Join us as we unravel the relationship between these two widely used temperature scales and explore their practical applications in various industries.
Throughout this exploration, we’ll trace the historical evolution of Celsius and Fahrenheit scales, uncovering the reasons behind their development and global adoption. Dive into a comparative analysis of these scales, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages, and equip yourself with the knowledge to confidently navigate temperature conversions.
Temperature Conversion
Temperature is a measure of the warmth or coldness of an object. It is an important concept in many areas of science, engineering, and everyday life. The two most common temperature scales are the Celsius scale and the Fahrenheit scale.
Relationship between Celsius and Fahrenheit
The Celsius scale is based on the freezing and boiling points of water. Water freezes at 0 degrees Celsius (°C) and boils at 100 °C. The Fahrenheit scale is based on the freezing and boiling points of a mixture of water and salt.
Water freezes at 32 degrees Fahrenheit (°F) and boils at 212 °F.
Formula for Converting Celsius to Fahrenheit, 260 celsius to fahrenheit
To convert a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit, you can use the following formula:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Significance of Freezing and Boiling Points
The freezing and boiling points of water are important reference points for both the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales. These points help to define the scale and make it easy to compare temperatures. For example, if you know that water freezes at 0 °C and boils at 100 °C, you can easily determine the temperature of a room by measuring the temperature of a glass of water.
Applications of Temperature Conversion
Temperature conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit is widely used in various industries and fields, playing a crucial role in scientific research, engineering, meteorology, and everyday life.
Converting between these scales is essential for accurate measurements, ensuring compatibility of devices, and facilitating communication across different regions and disciplines.
260 degrees Celsius is equivalent to about 500 degrees Fahrenheit. This is a very high temperature, and it is important to note that cooking chicken to this temperature will result in a very dry and overcooked product. The ideal internal temperature for a cooked chicken leg is between 165 and 175 degrees Fahrenheit, which is much lower than 260 degrees Celsius.
For more information on the internal temperature of chicken legs, please refer to this article .
Industries and Fields
- Meteorology:Temperature conversion is critical in weather forecasting, where temperatures are often reported in both Celsius and Fahrenheit to cater to different audiences.
- Engineering:Temperature conversion is crucial in designing and operating industrial machinery, as different components may operate at specific temperature ranges measured in either Celsius or Fahrenheit.
- Food Science:Cooking recipes and food safety guidelines often specify temperatures in both Celsius and Fahrenheit, ensuring accuracy and consistency in food preparation and preservation.
- Medicine:Temperature conversion is essential in medical settings, such as monitoring body temperature and administering medications, where precise temperature measurements are vital.
Devices and Instruments
- Thermometers:Thermometers can be calibrated to display temperatures in either Celsius or Fahrenheit, allowing users to choose the scale most suitable for their application.
- Ovens and Stoves:Cooking appliances often feature both Celsius and Fahrenheit settings, enabling users to adjust the temperature based on recipe requirements or personal preferences.
- Scientific Equipment:Laboratory equipment, such as spectrophotometers and incubators, may require temperature settings in specific units, necessitating conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit.
- Weather Stations:Weather stations collect and report temperature data in both Celsius and Fahrenheit, catering to a wider audience and facilitating comparisons across different regions.
Historical Context of Temperature Scales
The history of temperature scales is a fascinating journey that spans centuries and cultures. The development of the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales, the two most widely used temperature scales today, was driven by the need for accurate and standardized methods of measuring temperature.
The Celsius scale was developed by the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in 1742. Celsius initially defined the scale with 0 degrees representing the boiling point of water and 100 degrees representing the freezing point of water. However, after his death, the scale was inverted, with 0 degrees representing the freezing point and 100 degrees representing the boiling point.
Adoption of the Celsius Scale
- The Celsius scale gained widespread acceptance in Europe during the 19th century.
- In 1948, the International Committee for Weights and Measures (CIPM) adopted the Celsius scale as the international standard for temperature measurement.
- Today, the Celsius scale is the most commonly used temperature scale in the world, with the exception of the United States.
The Fahrenheit scale was developed by the German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1724. Fahrenheit initially defined the scale with 32 degrees representing the freezing point of water and 96 degrees representing the normal human body temperature. However, after his death, the scale was redefined, with 32 degrees representing the freezing point of water and 212 degrees representing the boiling point of water.
Adoption of the Fahrenheit Scale
- The Fahrenheit scale gained widespread acceptance in the United States during the 19th century.
- Today, the Fahrenheit scale is still commonly used in the United States, although the Celsius scale is becoming increasingly popular.
Comparison of Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
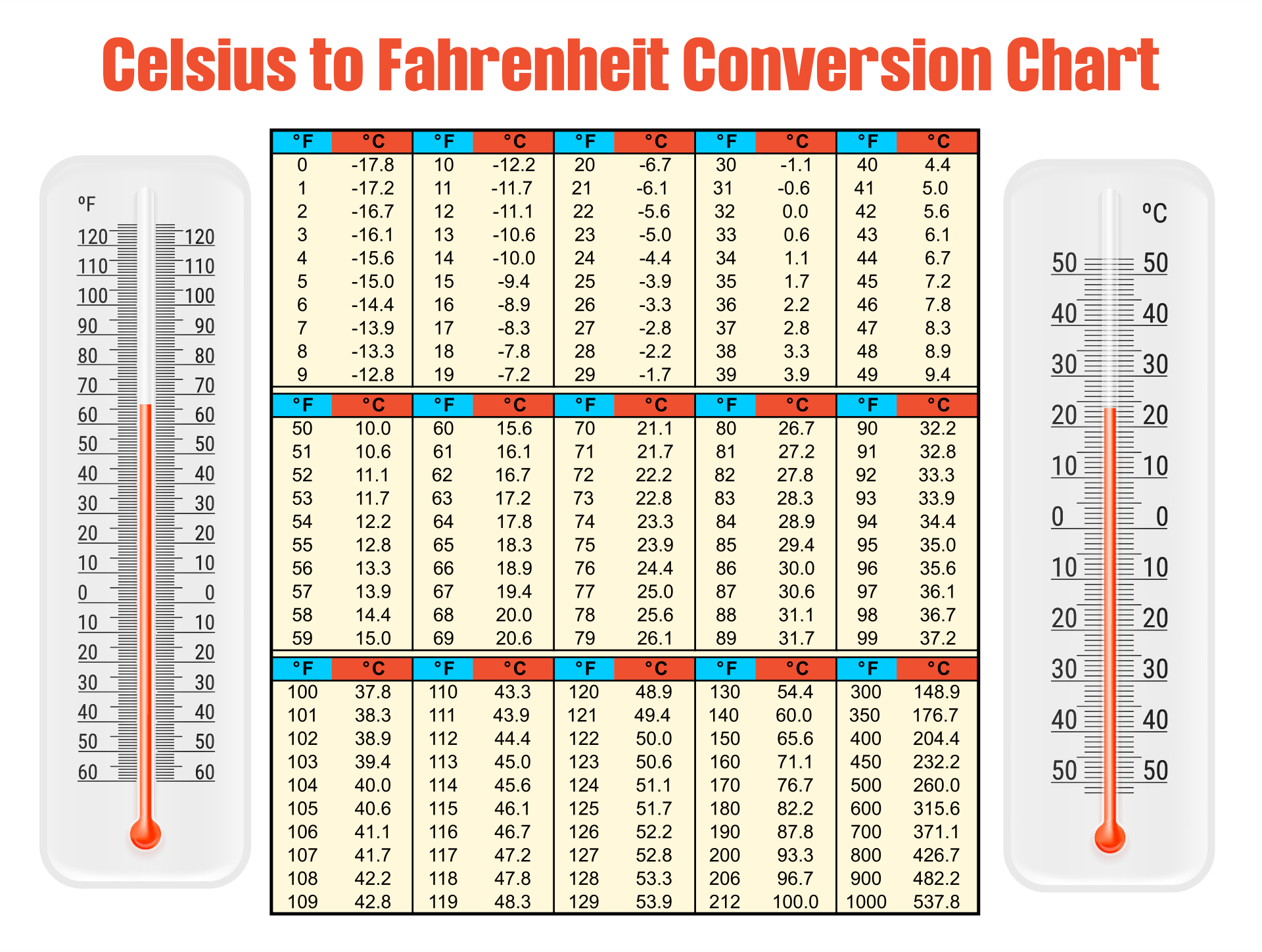
The Celsius and Fahrenheit scales are two of the most commonly used temperature scales in the world. Both scales are based on the freezing and boiling points of water, but they use different units to measure temperature.
The Celsius scale is a metric scale, which means that it uses the decimal system. The freezing point of water is 0 degrees Celsius, and the boiling point of water is 100 degrees Celsius. The Celsius scale is widely used in scientific research and in most countries around the world.
The Fahrenheit scale is a non-metric scale, which means that it does not use the decimal system. The freezing point of water is 32 degrees Fahrenheit, and the boiling point of water is 212 degrees Fahrenheit. The Fahrenheit scale is primarily used in the United States and a few other countries.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
The Celsius scale is often preferred by scientists because it is a metric scale and because it uses the freezing and boiling points of water as its reference points. The Fahrenheit scale is often preferred by people in the United States because it is the scale that they are most familiar with.
Here is a table comparing the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales:
| Scale | Freezing Point | Boiling Point | Common Temperature Ranges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Celsius | 0°C | 100°C | 0°C to 30°C (freezing to room temperature) |
| Fahrenheit | 32°F | 212°F | 32°F to 90°F (freezing to room temperature) |
Practical Examples and Exercises
Engage in a series of exercises designed to enhance your understanding of temperature conversion.
Follow the step-by-step instructions to solve each problem, ranging from beginner-friendly to challenging.
Beginner Exercises
- Convert 25 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit.
- Find the Fahrenheit equivalent of
10 degrees Celsius.
- A recipe calls for baking at 180 degrees Celsius. What is this temperature in Fahrenheit?
Intermediate Exercises
- A weather forecast predicts a high of 95 degrees Fahrenheit. Express this temperature in Celsius.
- A scientific experiment requires a temperature of273.15 degrees Celsius. Convert this to Fahrenheit.
- A medical procedure involves maintaining a body temperature of 37 degrees Celsius. What is this temperature in Fahrenheit?
Advanced Exercises
- A laboratory experiment involves heating a substance from78 degrees Celsius to 122 degrees Fahrenheit. Determine the temperature change in both Celsius and Fahrenheit.
- A recipe calls for preheating an oven to 425 degrees Fahrenheit. If the oven is calibrated in Celsius, what temperature should be set?
- A weather forecast predicts a temperature range of15 degrees Celsius to 10 degrees Celsius. Express this range in Fahrenheit.
Last Point: 260 Celsius To Fahrenheit
As we conclude our exploration of 260 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion, we hope you’ve gained a deeper understanding of temperature scales and their significance. Remember, temperature conversion is not merely a mathematical exercise but a valuable tool in scientific research, engineering, cooking, and countless other fields.
Embrace the knowledge you’ve acquired and continue to explore the fascinating world of temperature measurement.

