What makes eggs smell when cooked – When the aroma of eggs fills the air, it signals the start of a culinary journey. But what is it that gives eggs their distinctive smell when cooked? Join us as we embark on a tantalizing exploration into the science behind the symphony of flavors and aromas that make eggs a beloved breakfast staple.
From the intricate chemical composition of eggs to the transformative effects of cooking methods, we will unravel the secrets that lie behind the olfactory experience of eggs. Along the way, we will uncover the factors that influence egg odor intensity and delve into the potential health implications associated with strong egg odors.
Chemical Composition of Eggs
Eggs are a nutritious food source composed of various chemical components that contribute to their distinct characteristics, including their odor when cooked.
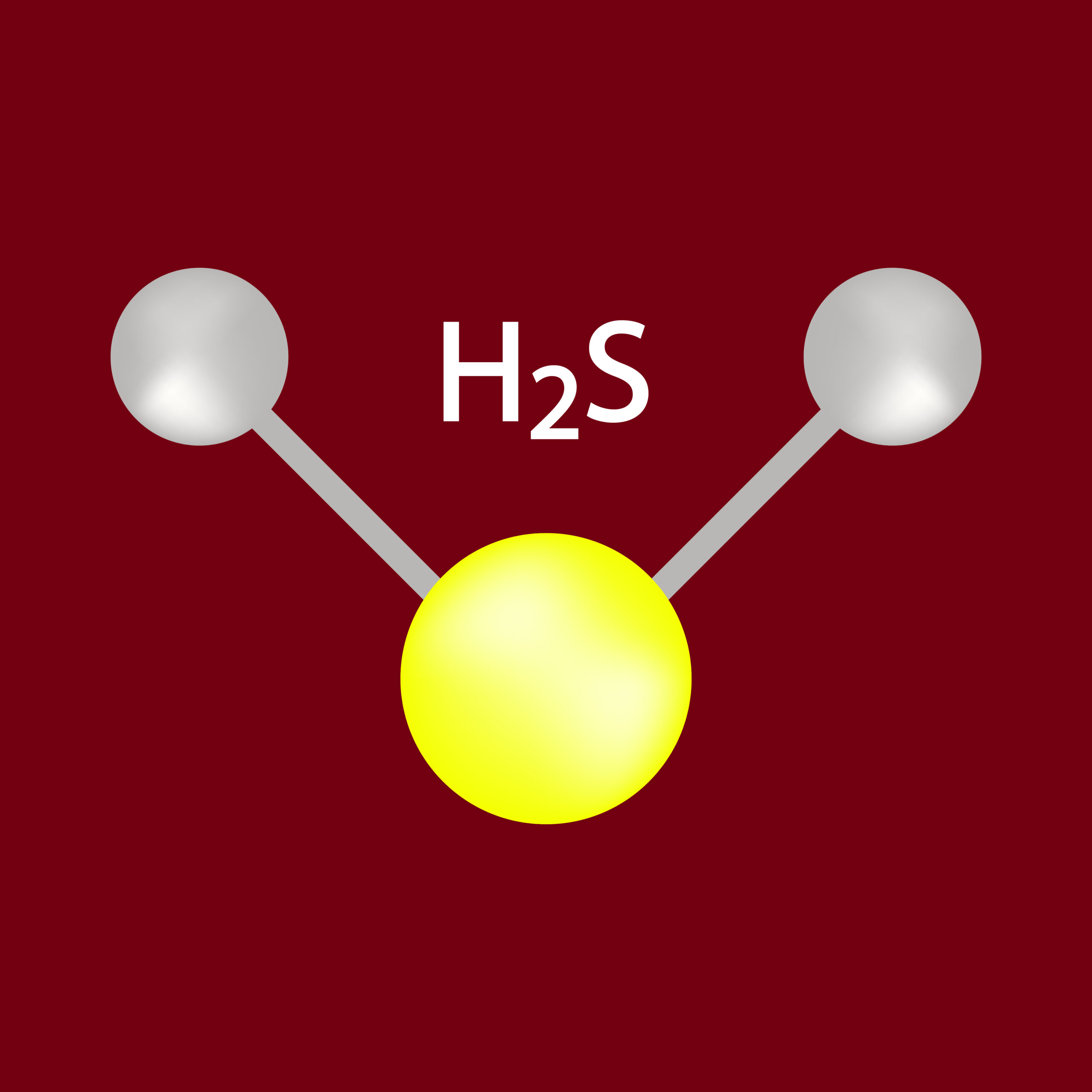
Egg whites, in particular, contain sulfur-containing amino acids, such as cysteine and methionine. These amino acids are responsible for the production of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas when eggs are cooked.
Role of Hydrogen Sulfide, What makes eggs smell when cooked
Hydrogen sulfide is a colorless gas with a pungent, rotten-egg odor. When eggs are heated, the sulfur-containing amino acids break down, releasing H2S gas. This gas is the primary contributor to the characteristic smell of cooked eggs.
Other Sulfur-Containing Compounds
In addition to hydrogen sulfide, other sulfur-containing compounds present in eggs, such as dimethyl sulfide and dimethyl disulfide, also contribute to the overall odor profile of cooked eggs. These compounds have distinct aromas that add complexity to the egg’s smell.
Factors Influencing Egg Odor Intensity
The intensity of egg odor during cooking is influenced by various factors, including freshness, storage conditions, breed, and diet of the hens.
Egg Freshness
As eggs age, their freshness deteriorates, and this can affect their odor. Fresh eggs have a mild, neutral smell, while older eggs may develop a stronger, more sulfurous odor due to the breakdown of proteins and the release of hydrogen sulfide gas.
Storage Conditions
The storage conditions of eggs can also impact their odor. Eggs should be stored in a cool, humid environment, ideally in the refrigerator. Exposure to high temperatures or excessive moisture can promote bacterial growth and the production of off-odors.
When eggs are cooked, the sulfur compounds in the egg white react with the heat to produce hydrogen sulfide gas. This gas has a strong, unpleasant smell. The higher the temperature at which the eggs are cooked, the more hydrogen sulfide gas is produced.
For example, if you cook an egg at 220 degrees Celsius ( 220 degrees celsius to fahrenheit ), it will produce more hydrogen sulfide gas than if you cook it at a lower temperature. This is why eggs that are cooked at high temperatures often have a stronger smell than eggs that are cooked at lower temperatures.
Breed and Diet
The breed of hen and its diet can influence the odor of eggs. Certain breeds, such as Araucana and Ameraucana hens, lay eggs with a distinctive greenish-blue shell and a stronger odor compared to eggs from other breeds. The diet of hens can also affect egg odor, with diets rich in sulfur-containing compounds, such as garlic or onions, resulting in eggs with a more pronounced sulfurous odor.
Health Implications of Egg Odor
Consuming eggs with strong odors can pose potential health concerns. These odors may indicate the presence of harmful bacteria or other contaminants that can cause foodborne illnesses. Eggs with a strong sulfurous, sour, or rotten smell should be discarded immediately, as they may contain high levels of bacteria such as Salmonella or E.
coli. These bacteria can cause symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps.In contrast, eggs with mild odors may be safe to consume. A slightly sulfuric or eggy smell is often associated with older eggs but does not necessarily indicate spoilage.
However, if the odor is accompanied by other signs of spoilage, such as a slimy texture or discoloration, the egg should be discarded.To identify eggs that are safe to consume based on odor, it is essential to rely on your senses.
Trust your nose and discard any eggs with strong or unpleasant odors. Fresh eggs should have a neutral or slightly eggy smell. If you are unsure about the safety of an egg, it is always better to err on the side of caution and discard it.
Closing Summary: What Makes Eggs Smell When Cooked
As we conclude our culinary adventure, we have gained a deeper appreciation for the complex interplay of chemistry, cooking techniques, and freshness that shape the olfactory experience of eggs. Whether you prefer the subtle fragrance of gently boiled eggs or the robust aroma of fried eggs, understanding the science behind egg odor empowers us to make informed choices and savor the full spectrum of flavors that eggs have to offer.

