250 c en f – Embark on a temperature conversion journey as we delve into the world of 250 Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion. Discover the formula, explore practical applications, and unravel the historical context behind these two widely used temperature scales.
Conversion Basics: 250 C En F
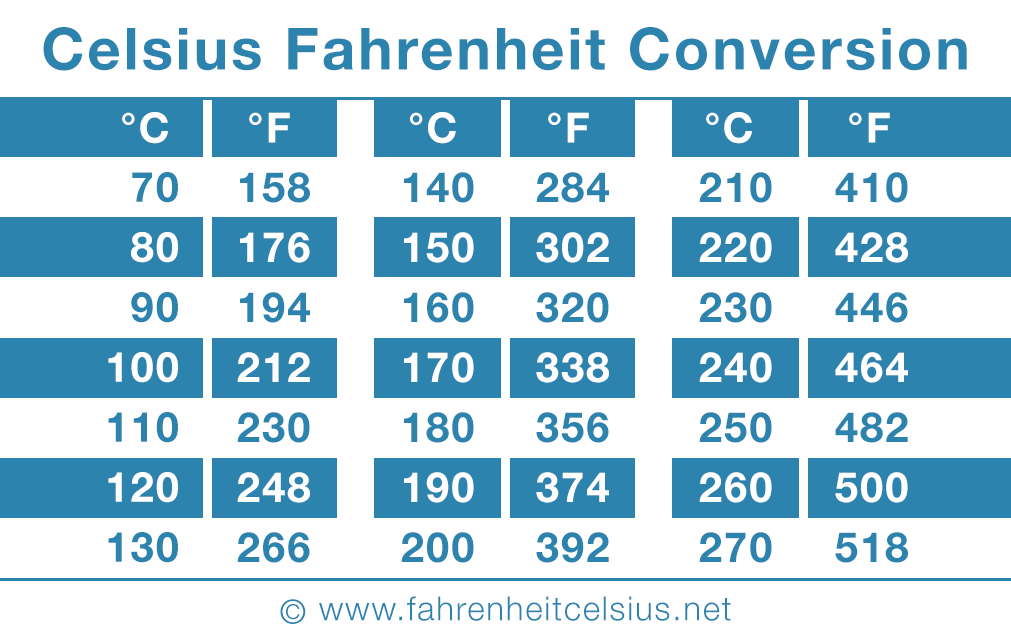
Temperature conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a common task in various scientific and everyday situations. Understanding the concepts behind this conversion is crucial for accurate temperature measurements.
The conversion formula from Celsius to Fahrenheit is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
This formula involves multiplying the Celsius temperature by 9/5 and then adding 32 to the result.
Significance of Freezing and Boiling Points
The freezing and boiling points of water play a significant role in temperature scales. On the Celsius scale, water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C. On the Fahrenheit scale, water freezes at 32°F and boils at 212°F. These specific temperatures serve as reference points for calibrating thermometers and establishing temperature standards.
Temperature Range
Temperature range refers to the difference between the highest and lowest temperatures experienced in a given context, such as human comfort, room conditions, or extreme weather events. Understanding temperature ranges is crucial for various applications and industries, including heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), meteorology, and climate science.
Human Comfort Range
The human comfort range is the temperature range within which most people feel comfortable without experiencing excessive heat or cold. This range varies depending on factors such as humidity, air movement, and personal preferences. Generally, the comfort range falls between:
- Celsius:20-25°C (68-77°F)
- Fahrenheit:68-77°F (20-25°C)
Room Temperature Range, 250 c en f
Room temperature refers to the temperature maintained within an enclosed space, typically a building or room. The ideal room temperature range for human comfort is similar to the human comfort range, but it may vary slightly depending on the purpose of the room and the activities conducted within it.
Common room temperature ranges include:
- Celsius:21-24°C (70-75°F)
- Fahrenheit:70-75°F (21-24°C)
Extreme Weather Temperature Range
Extreme weather conditions can involve temperatures that fall far outside the human comfort range. These conditions can pose significant health risks and impact various industries and infrastructure. Examples of extreme weather temperature ranges include:
- Celsius:Below -40°C (-40°F) or above 50°C (122°F)
- Fahrenheit:Below -40°F (-40°C) or above 122°F (50°C)
Understanding temperature ranges is essential for designing and operating HVAC systems, forecasting weather conditions, and mitigating the effects of extreme weather events. By considering the temperature ranges associated with human comfort, room conditions, and extreme weather, we can create and maintain comfortable and safe environments while adapting to the challenges posed by varying temperatures.
250°C is a common temperature for baking. If you’re looking for a delicious and healthy side dish to serve with your meal, try this broccoli and cauliflower salad recipe . It’s easy to make and packed with flavor. You can also adjust the temperature to 250°F if you prefer a lower heat setting.
Applications of Conversion
Celsius-to-Fahrenheit conversion plays a crucial role in various practical applications across different fields.
Accurate conversion is essential in fields such as cooking, meteorology, and scientific research, where precise temperature measurements are critical for successful outcomes. Conversion errors can significantly impact the quality of food, weather forecasts, and research findings.
Cooking
In cooking, accurate temperature conversion is essential for precise baking and cooking. Recipes often specify temperatures in Fahrenheit or Celsius, and converting between the two units ensures the correct temperature is achieved for optimal results.
- For example, a cake recipe calling for 350°F (177°C) requires precise conversion to ensure the cake bakes evenly and has the desired texture.
Meteorology
In meteorology, accurate temperature conversion is crucial for weather forecasting. Weather reports and forecasts often use both Celsius and Fahrenheit, and conversion allows meteorologists to interpret and communicate temperature data effectively.
- For instance, a weather forecast predicting a high of 95°F (35°C) can be easily converted to Celsius for individuals who are more familiar with the metric system.
Scientific Research
In scientific research, accurate temperature conversion is essential for replicating experiments and ensuring the validity of findings. Scientific literature often reports temperatures in both Celsius and Fahrenheit, and conversion allows researchers to compare and analyze data from different sources.
- For example, a study on the effects of temperature on enzyme activity may report results in both Celsius and Fahrenheit, requiring conversion for cross-referencing with other research.
Historical Context
The Celsius and Fahrenheit scales, two widely used temperature measurement systems, have distinct origins and development paths.
In the mid-18th century, Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius developed the Celsius scale, initially known as the centigrade scale. He defined 0°C as the freezing point of water and 100°C as its boiling point. This scale was later refined by other scientists, including Jean-Pierre Christin, who inverted the scale in 1743 to its current form.
Adoption of Different Scales
The Fahrenheit scale, created by German physicist Daniel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, was initially based on the freezing and boiling points of a mixture of water and salt. Fahrenheit set 32°F as the freezing point of water and 212°F as its boiling point.
This scale gained popularity in English-speaking countries, while the Celsius scale became more prevalent in Europe and most other parts of the world.
Ongoing Use and Relevance
Both the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales continue to be used today, with the Celsius scale being the more commonly accepted scientific standard. The Fahrenheit scale is still widely used in the United States, Belize, the Cayman Islands, and a few other countries.
The ongoing use of both scales can be attributed to factors such as cultural familiarity, established infrastructure, and industrial standards.
Final Wrap-Up
Mastering the conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit empowers you to navigate temperature-related tasks with confidence. Whether you’re cooking a culinary masterpiece, forecasting the weather, or conducting scientific research, accurate conversion ensures precise outcomes.

